Arthritis and arthrosis are complex diseases that affect the joints. Due to similar symptoms, many people think that these diseases are identical, but they are not. Arthritis and arthrosis differ in the causes of the disease, in the nature of its development, in the area of damage and require completely different treatment.
Suppose two people see a doctor complaining of joint pain. One was diagnosed with arthritis and the other with arthrosis. While the two patients lined up, they had time to discuss their health problems a little.
It was found that their symptoms are very similar: the joints hurt, they do not bend / unfold at full strength, they do not give rest either at night or during the day. Even diagnoses are consonant, but they are still different. What is the difference between arthritis and osteoarthritis if both diseases affect the joints?
What is arthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joint. It is always preceded by damage to bone or cartilaginous tissue by some factor.
Biologically active substances are released from the destroyed cells, which triggers an inflammatory reaction. The vessels of the lesion expand, fill with blood: because of this, cells of the immune system appear in the articular tissue to fight the harmful factor.
At the same time, the liquid part of the blood leaves the vascular bed and edema forms, which limits the area of inflammation. This is how the body protects itself from extensive damage by bacteria, foreign bodies and chemicals.
After complete or partial elimination of the pathogen, the healing mechanism begins. If the damage is less, normal tissue function is restored. Deep defects heal through a scar - an area of rough connective tissue that does not perform the normal function of an organ.
Arthritis goes through all these stages:
- alteration - damage; exudation
- - the formation of edema;
- proliferation - cure.
Reasons
The causes of the disease are great, let's list the main ones:
- Streptococcal infection
- (tonsillitis, scarlet fever) often gives rise to a complication - rheumatism;
- aggressive autoantibodies - proteins that the body produces to fight against its own tissues; this situation develops with an error in the immune defense, by which she perceives the joints as an element foreign to the body - rheumatoid arthritis;
- violation of purine metabolism leads to deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints - gout;
- Allergic reactions can involve the tissue of the joints with the development of an inflammatory reaction - allergic arthritis;
- prolonged use of certain medications causes inflammation (isoniazid, D-penicillins, hydralazine, orifices) - medication arthritis; The bacteria
- is carried in the bloodstream or during surgery - infectious arthritis;
- a viral or bacterial infection of any location can indirectly affect the tissues of the joints - this is reactive arthritis;
- acute trauma - recent damage (impact, hematoma, capsule rupture).
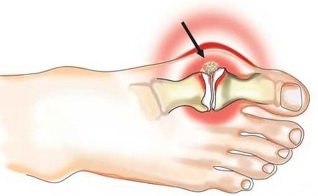
Symptoms
The disease is characterized by an acute initial stage, that is, in a context of full health, the individual has acute pain in the joint. For autoimmune forms, symmetrical damage to small joints is characteristic - interphalangeal in the fingers, wrist, elbow.
Gout, in the vast majority of cases, begins with inflammation of the joint between the thumb and the foot. In bacterial and reactive arthritis, the large joints are usually affected on one side: knee, hip, sacrum (at the junction of the spine with the pelvic bones).
Rheumatism develops in a context of fever and general weakness, usually preceded by angina. Severe inflammation of the bone, cartilage and synovial membrane with fever may occur, general intoxication: headache, weakness, lack of appetite.
The skin over the joint becomes red and hotter than other areas. Externally, it looks swollen and swells. If the injury occurred on only one side, then the difference between a healthy and a sick member is visible.
Restricted movement is associated with swelling and pain. If the joint cavity is slightly inflamed, it works almost completely. With a pronounced pathological reaction, the entire synovial cavity can be filled with liquid - in this case, mobility is severely limited.
Treatment
Treatment is performed by a general practitioner, rheumatologist or traumatologist - if the cause is mechanical damage. The therapy aims to eliminate the provocation factor and stop the inflammation.
For bacterial and reactive arthritis, antibiotics are needed, for autoimmune - cytostatics or glucocorticoids, for allergic - glucocorticoids and antihistamines.
The inflammatory fluid is removed with a syringe or special suction during arthroscopy. The joint is immobilized throughout the period of acute inflammation. Therapeutic exercises are shown after the patient to restore joint mobility.
Medical advice
From the personal practice and work experience of colleagues - with inflammation in the joints of any etiology, gelatin compresses have been shown to be good. They are simple to implement and inexpensive. It is necessary to fold the gauze in several layers, the length and width must be sufficient for the painful joint. Dip the folded gauze in hot water, squeeze, straighten. Pour a thin layer of gelatin on top, roll it so that it stays inside, like a bag, and does not drain. Apply over the joint, wrap with polyethylene bag on top, fix with bandage and / or adhesive tape. You can use a compress for up to 3 hours, do it twice a day for 2 weeks. Usually, the effect is felt on the 4-5th day of use, but therapy must be continued to achieve the desired result, if the course is interrupted, the pain will return.
What is arthrosis
Arthrosis (otherwise, osteoarthritis) is a degenerative dystrophic disease. It is based on the deterioration of the articular cartilage nutrition, the slowdown of its recovery and the gradual thinning.
Simply put, the cartilage layer wears out faster than it rebuilds. The articular surfaces of the bone are exposed. They are not as smooth as cartilage and they rub hard on each other during movement. Bone plaques are partially destroyed, with weak chronic inflammation developing.
As the disease progresses, bone spines grow in the joint - a protective tissue response to permanent damage. They interfere with the sliding of the surfaces with each other and the mobility of the joint is impaired.
Osteoarthritis in most people starts to progress after 30-40 years, lasts for years, its symptoms are mild or moderate.
Osteoarthritis of the vertebral joints is generally called osteochondrosis.
Reasons
There are predisposing factors that cause the development of the pathology at an early age and complicate its course:
- intense physical activity in athletes;
- obesity;
- history of joint damage; vascular disease
- ;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- violation of the normal configuration of the joint, for example, with flat feet;
- prolonged exposure to vibration;
- in women - hormonal imbalance or menopause.
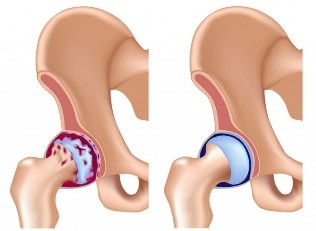
Symptoms
Large joints on one side are usually affected: knee, hip, sacrum. The disease begins imperceptibly. At first, pain is rare and is associated with significant physical exertion.
Unpleasant feelings disappear in the same day or in a few days if the person can rest. As the disease progresses, the intensity of the pain increases, it occurs even with normal daily stress.
The mobility of the joint gradually decreases and as a result of the disease it is completely lost. The movements of the diseased limb cause severe pain. Osteoarthritis can be made worse by arthritis - the fluid accumulates in the joint cavity, the skin above it is red and hot. After the inflammatory reaction has disappeared, the disease course returns to the previous course.
Treatment
Arthrosis is treated by a traumatologist, orthopedist, sometimes a surgeon. The therapy aims to restore the metabolic processes in the cartilage, improve the nutrition of the joints and eliminate the inflammatory response. Treatment is lifelong, can be continuous or with medication.
In the interictal period, chondroprotectors are prescribed in the form of pills and ointments, therapeutic exercises, massages. With an exacerbation, chondroprotectors are administered intravenously or intramuscularly together with analgesics and anti-inflammatories. A traumatologist can inject protective drugs directly into the joint every few months.
Advanced stages of the disease require surgical intervention, during which the diseased joint is replaced by an artificial one.
Differences between diseases
| Resource | Arthritis | Arthrosis |
| Cause of the disease | Inflammation | Cartilage degeneration |
| Flow | Acute, chronic with exacerbations | Chronic |
| Pain | Intense from the start, more pronounced in the morning | At the beginning of the disease, weak, gradually increasing. It intensifies at night and after the effort |
| Movements | It is necessary to "disperse" - in the morning, after sleeping, the joints are less mobile | Mobility gradually decreases, without morning stiffness |
| Affected joints | Small joints of the hands and feet are affected symmetrically. The big ones suffer from bacterial infection | One or more large joints on different sides of the body |
| Blood test | Serious inflammatory changes in the general blood test, rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, antibodies to pathogens | No typical changes |
| X-ray | Gradual changes, osteoporosis - bone loss, cysts in the bones | Gradual changes, deformation of the joint space, appearance of spines and bony protuberances. |
| Basic Treatment | Anti-inflammatories | Chondroprotectors |
A similar characteristic of both diseases is a progressive course with a gradual loss of mobility. Autoimmune arthritis often manifests itself at a young age, when the person is still frivolous with his health.
It should be remembered that any joint pain that lasts for a long time occurs under certain conditions - this is a serious reason to see a doctor. It is important to diagnose the disease in time and start treatment in order to delay the development of the pathological process.



































